Copyright © 2024, supplementsvilla.com
14 Mar 2024 HEALTH TIPS
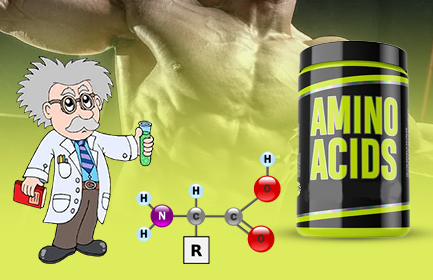
Amino acids are the building blocks of life, playing essential roles in numerous biological processes within the human body. From supporting muscle growth and repair to facilitating neurotransmitter amino acids are integral to our health and well-being. In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve into the science behind amino acids, exploring their structure, functions, sources, and importance in maintaining optimal health.
Understanding Amino Acids: The Basics
Amino acids are organic compounds composed of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and sometimes sulfur. They are classified into three categories based on their structure and properties:
Functions of Amino Acids in the Body
Amino acids play a variety of critical roles in the body, including:
Dietary Sources of Amino Acids
Amino acids are found in a wide variety of foods, both animal and plant-based. Animal sources such as meat, poultry, fish, eggs, and dairy products are particularly rich in protein and contain all nine essential amino acids in varying proportions. Plant-based sources of protein include legumes (beans, lentils, chickpeas), grains (quinoa, rice, wheat), nuts, seeds, and soy products (tofu, tempeh, soy milk).
Importance of Essential Amino Acids
While all amino acids are important for overall health, essential amino acids are particularly crucial because the body cannot produce them on its own. Therefore, it's essential to obtain these amino acids through dietary sources to ensure optimal health and function. Consuming a balanced diet that includes a variety of protein-rich foods can help ensure an adequate intake of essential amino acids.
Supplementation and Amino Acids
In certain situations, such as intense exercise, illness, or a restrictive diet, supplementation with amino acids may be beneficial. Branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs), which include leucine, isoleucine, and valine, are popular supplements among athletes and fitness enthusiasts for their role in muscle protein synthesis and recovery. Other amino acid supplements, such as glutamine and arginine, are often used to support immune function, gut health, and exercise performance.
Conclusion
Amino acids are the building blocks of life, playing essential roles in countless physiological p…